Table of contents
1. Hormone-Free Birth Control Methods
2. Breastfeeding As Birth Control
3. Hormonal Birth Control Options
Being a new mom is hugely rewarding, but it comes with endless decision-making, like figuring out birth control while breastfeeding. There is no doubt that breastfeeding provides unmatched benefits for both you and your baby, and the postpartum stage can be a period of great joy. But realistically, another pregnancy may be the last thing on your mind as you take the time to heal and care for your newborn.
There are many safe and effective contraception options with and without hormones that you can start right away, even as you establish your breastfeeding routine.
Hormone-Free Birth Control Methods
Non-hormonal birth control can prevent pregnancy without harming your baby's growth and development or the quantity or quality of your breast milk. Here are some hormone-free options you should consider:
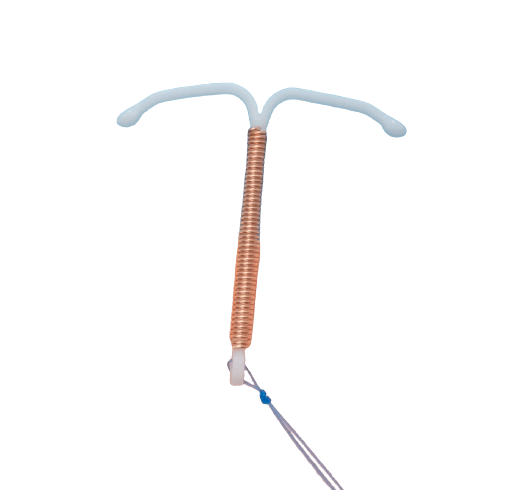
Copper IUD
The copper IUD (Paragard) is the most effective hormone-free contraception. It can be inserted into your uterus right after vaginal or cesarean birth. Once in place, this small "T" shaped device can remain in place for up to 10 years or until you are ready to expand your family. You may experience side effects like cramps or bleeding between periods during the first few months with your IUD, but these symptoms usually go away within a year.

Condoms
Condoms are available with or without spermicide and are worn internally (in the vagina) or externally (over the penis). The external condom is a thin sheath of latex, polyurethane, or natural membrane. In comparison, the internal condom (a thin plastic pouch) lines the vagina and is held in place by a closed inner ring at the cervix and an outer ring at the opening of the vagina.
You might find that your vagina becomes dryer than usual, while nursing and using a condom can cause some irritation. If this happens, use a water or silicone-based lubricant along with your condom to decrease soreness. Also, avoid any oil-based lubricants like baby oil or petroleum jelly when using latex condoms since this can cause the condom to tear or break.
Diaphragm, Cervical Cap, or Sponge
You can choose the diaphragm, cervical cap, or sponge as your preferred contraception six weeks after giving birth when your uterus and cervix have returned to their normal size.
Diaphragm: This reusable dome-shaped cup is made of latex or silicone. It fits inside your vagina and covers your cervix. The traditional diaphragm comes in different sizes that your healthcare provider must fit. The newer version (Caya diaphragm) comes as a one-size-fits-all. The diaphragm must be used with spermicide and left in place for 6 hours after sex but no more than 24 hours total.
The cervical cap: Prescribed and fitted by your doctor, this flexible rubber cap fits tightly over the cervix. Like the diaphragm, the cap should be used with a spermicide and left in place for 6 hours after sex, but no more than 48 hours total.
Your provider should refit your cervical caps after pregnancy, weight loss, weight gain, or a vaginal birth since the fit may change.
The Sponge: This soft round foam that contains spermicide covers your cervix to keep sperm from entering the uterus. It can be put in place up to 24 hours before sex and left in place for at least 6 hours after sex. But you should not wear the sponge for more than 30 hours total.
Even though the cap and sponge are great options, it is essential to note that they are less effective in preventing pregnancy in women who have given birth.
Breastfeeding As Birth Control
Lactational amenorrhea (LAM): The hormones that produce your breast milk will also work to stop your ovaries from releasing an egg. For LAM to be effective:
· Your baby must be under 6 months of age
· You must not have had a period
· You must exclusively breastfeed your baby at least every 4 hours during the day and at least every 6 hours at night with no long intervals between feeds
LAM is approximately 98 percent effective in preventing pregnancy but pumping, feeding your baby formula, or feeding your baby other foods or drinks will lessen the effectiveness.
Tubal sterilization: Having your "tubes tied" is a permanent form of birth control. During the procedure, both fallopian tubes are blocked or cut. Your doctor can complete this surgical procedure right after your delivery. Breastfeeding will only be affected if general anesthesia is needed since this medicine can be passed through your breast milk.
This birth control is permanent so, be sure that you no longer want to get pregnant again since there is no guarantee that attempts to reverse the procedure will work.
Hormonal Birth Control Options
Using birth control with hormones will not harm your baby. Still, experts recommend that you hold off on using hormonal contraceptives that contain estrogen during the first 6 weeks after giving birth because of your increased risk of blood clots and the potential effects they have on breastfeeding performance. But there are many other alternatives available:
Hormonal IUD
A provider places this small T-shaped device inside the uterus. It releases a small amount of progestin into your uterus each day to prevent pregnancy. The hormonal IUD can remain in place for 3 to 6 years, depending on the device selected.
You may experience spotting and irregular bleeding during the first 3 to 6 months while using a hormonal IUD, or your period may stop altogether. Other side effects you may experience include headaches, nausea, depression, and breast tenderness.
Implant
The birth control implant is a single thin, flexible progestin-based rod inserted under the skin of your upper arm. It can be inserted by your healthcare provider immediately after your vaginal or cesarean birth. The implant can stay in place for over 3 years. You may experience lighter, heavier, more extended periods or bleeding between periods.
Depo Provera
"The shot" contains a type of progestin and works by preventing ovulation. You can get your first shot right after your vaginal or cesarean delivery. After that, you will continue to see your health care professional every three months to receive your shot.
Birth Control Pills for Breastfeeding Moms
Birth control pills with high estrogen levels are more likely to decrease milk supply. But, progestin-only birth control pills (the mini-pill) only contain progestin and can be taken right after birth. Each pill must be taken at the same time each day for maximum effectiveness. If you miss a pill by more than 3 hours, you will need to use a backup method for the next 48 hours.
A small amount of the progestin hormone passes into your breast milk, but it won't harm your baby. Some studies suggest that the mini pill may positively affect the quantity and quality of your breast milk.
Contraception while Breastfeeding
There is a lot to consider when choosing the right birth control, especially while breastfeeding. Be sure to have an open and honest conversation with your healthcare provider to answer all your questions. Chances are, you will find an option that works best for you and your lifestyle.






