40% of women in the United States will develop a urinary tract infection (UTI) within their lifetime, while around 10% will get one every year. While UTIs generally aren't serious and tend to resolve quickly without any need for treatment, they're nonetheless uncomfortable and annoying.
One question that many people have is whether they can continue to have sex with a UTI. Although urinary tract infections are not a sexually transmitted infection, it's generally recommended that you abstain from sexual activity while recovering from a UTI. Let's take a closer look at why.
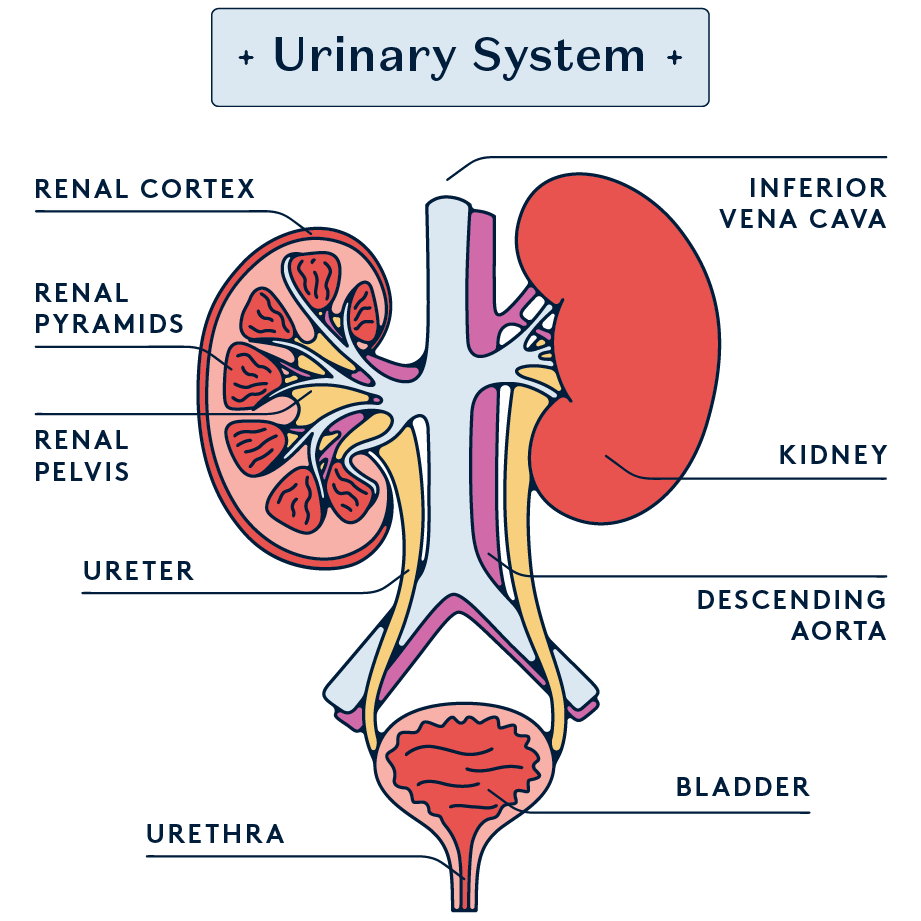
A urinary tract infection is an infection in any part of your urinary system, such as the kidneys, bladder, ureters, and urethra. UTIs affect women and AFAB folks four times as frequently as men and AMAB people, partly due to their shorter urethra and its positioning.
The most common cause of UTIs is the Escherichia coli bacteria (E. coli), which is found in the gastrointestinal tract. Urinary tract infections occur when these bacteria enter the urinary tract through the urethra and start multiplying in the bladder. Since the anus is close to the urethral opening in AFAB folks, E. coli can easily move from the GI tract to the urinary tract.
Symptoms of a UTI include:
- Painful urination
- Needing to pass urine more often or more urgently than normal
- Cloudy urine or blood in your urine
- Pain in your stomach or back
- A high temperature or a very low temperature
How are UTIs treated?
The primary treatment for UTIs is a course of antibiotics prescribed by your healthcare provider. The type and duration of antibiotic treatment can vary depending on the severity of the infection and the type of bacteria causing it. It's crucial to complete the entire course of antibiotics, even if symptoms improve before the medication is finished, to ensure the infection is fully eradicated and to prevent antibiotic resistance.
Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen can help alleviate some of the pain and discomfort associated with UTIs. Drinking plenty of water is also recommended as this helps dilute urine and encourages more frequent urination, which can help flush bacteria from the urinary tract
Sex with a UTI: common questions
How long should I wait to have sex after having a UTI?
Healthcare providers recommend waiting at least until after you've finished your antibiotic treatment and your symptoms have gone away. For an ordinary bladder infection, the antibiotics are usually taken for three to five days. More complicated UTIs like a kidney infection may require you to take antibiotics for up to two weeks.
Even if your symptoms disappear before you've finished the course of antibiotics, make sure to keep taking them for as long as advised. Stopping antibiotics early can contribute to antibiotic resistance, meaning that a future infection may be harder to control.
Can you pass a UTI to a partner during sex?
A UTI is not a sexually transmitted infection and isn't technically contagious. However, there's still a risk that you could pass the bacteria causing the urinary tract infection to your partner during sexual intercourse.
Will sexual intercourse make my UTI worse?
It's best to avoid vaginal penetration or anal sex while you have a urinary tract infection, as this can further spread bacteria. Additionally, penetrative sex can irritate the urethra and bladder, exacerbating the symptoms of a UTI. This irritation can increase discomfort, such as burning sensations, pelvic pain, and urinary urgency or frequency.
What can I still do with my partner while I have a UTI?
Of course, there are still many ways to maintain intimacy and connection with your partner without engaging in activities that could aggravate your UTI.
For example, non-penetrative sexual activities can be a way to maintain intimacy without putting pressure on the urinary tract. This includes activities like mutual masturbation, where there is no direct genital-to-genital contact. Just make sure to wash your hands thoroughly and pee before and after to reduce the risk of exacerbating the urinary tract infection. Giving oral or manual sex to the partner without a UTI is another way to remain sexually active without worsening the symptoms.
Alternatively, focusing on sensual touching, such as massages, gentle caresses, and other forms of affectionate physical contact can also be satisfying and help maintain a sense of intimacy with sexual partners.
Remember, every individual’s experience with a UTI can be different. If any sexual activity causes pain, discomfort, or seems to worsen UTI symptoms, it should be stopped immediately. The most important thing is to maintain open and honest communication with your partner to ensure everyone is comfortable.
How to prevent UTIs
To reduce your risk of urinary tract infections, here are some of the actions you can take:
- Hydration: Drink plenty of water to help dilute your urine and ensure you urinate regularly. This helps flush bacteria from your urinary tract before an infection can begin.
- Urinate When Needed: Don't hold urine for long periods. Urinating regularly can help expel bacteria from the urinary system.
- Urinate After Sex: To help clear any bacteria that may have entered the urethra during sexual activity, it's important to urinate soon after sexual intercourse. This includes manual and oral sex, not just penis-in-vagina intercourse.
- Proper Hygiene: Wipe from front to back after using the toilet to prevent bacteria in the anal region from spreading to the vagina and urethra.
- Consider Probiotics: Probiotics can help maintain healthy bacteria in your body, possibly aiding in the prevention of UTIs.
To find out more, check out our full blog post about how to treat and prevent UTIs.
Conclusion
In summary, while it's physically possible to have sex with a UTI, it's generally advisable to avoid it until you are symptom-free and have completed your treatment plan. Doing so helps ensure a faster recovery and reduces the risk of complications. Always consult with a doctor for personalised advice and treatment options for UTIs.
To take control of your sexual health, why not try the Daye vaginal screening? With our quick and easy at-home test kit, you can find out about how your vaginal microbiome impacts your risk of UTIs and sexually transmitted infections, and take steps to reduce the risk. Want to give it a go? Order your test kit today!